Belgium is a federal state comprising three communities, three regions, and four language areas. For each of these subdivision types, the sum of their circumscribed surfaces composes the entire country; in other words, the types overlap.
Regions of Belgium
 The language areas were established by the Second Gilson Act, which entered into force on August 2, 1963. The division into language areas was included in the Belgian Constitution in 1970.
The language areas were established by the Second Gilson Act, which entered into force on August 2, 1963. The division into language areas was included in the Belgian Constitution in 1970.
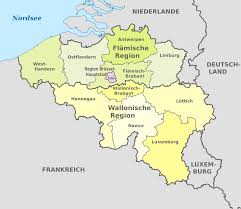
The Flemish Region (Flanders) and the Walloon Region (Wallonia) each comprise five provinces; the third region, Brussels-Capital Region, is not a province, nor does it contain any.
Together, these comprise 589 municipalities, which in general consist of several sub-municipalities (which were independent municipalities before a municipal restructuring in early 1977).
The communities, regions, language areas, municipalities, and provinces, are the five most important subnational entities of Belgium, as laid out in the Belgian constitution.
Lesser subnational entities include the intra-municipal districts, the administrative, the electoral and the judicial arrondissements, police districts, as well as the new inter-municipal police zones (lower level than the police districts).
All these entities have geographical boundaries: the language areas, the communities, the regions, the provinces and the municipalities. The language areas have no offices or powers and exist de facto as geographical circumscriptions, serving only to delineate the empowered subdivisions.
The institutional communities are thus equally geographically determined. Belgian Communities do not officially refer directly to groups of people but rather to specific political, linguistic and cultural competencies of the country. There is no subnationality in Belgium.
All Communities thus have a precise and legally established area where they can exercise their competencies:
- the Flemish Community has legal authority (for its Community competencies) only within the Dutch language area (which coincides with the Flemish Region) and bilingual Brussels-Capital language area (which coincides with the Region by that name);
- the French-speaking Community analogously has powers only within the French language area of the Walloon Region and in the Brussels-Capital Region, and the German Community in the German language area, which is a small part of the province of Liège in the Walloon region, and borders Germany.
The three regions are:
- the Brussels-Capital Region (Brussels)
- the Flemish Region (Flanders)
- the Walloon Region (Wallonia)
The three communities are:
- the Dutch-speaking Vlaamse Gemeenschap ("Flemish Community")
- the French-speaking Communauté Française ("French Community")
- the German-speaking Deutschsprachige Gemeinschaft ("German-speaking Community").
The four language areas (as taalgebieden in Dutch and Sprachgebiete in German), occasionally referred to as linguistic regions (from French régions linguistiques), are:
- the Dutch language area
- the Bilingual area Brussels-Capital
- the French language area
- the German language area (which has specific language facilities for French-speakers).