Geography of Aruba
20/11/2019
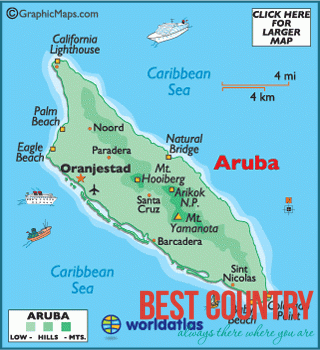
Aruba is a small Caribbean island (54 sq mi/140 km2) about the size of Washington, D.C., located 25 km north of the coast of Venezuela and 68 km northwest of Curaçao, the largest island of the Kingdom of the Netherlands.
Aruba’s terrain is mostly flat with a few hills. There is little in the way of vegetation or outstanding physical features and no inland water. Aruba’s best-known geographical feature is its white-sand beaches, which are the basis of an active tourism industry that is the mainstay of the island’s economy. Aruba is situated on the Caribbean Tectonic Plate. The island is made up of limestone-capped hills and ridges, with cliffs on the northern and northeastern coasts and coral reefs on the southern coast.
Mountains and Hills
Aruba’s terrain is almost entirely flat. The highest elevation, so-called Mount Jamanota, is only 188 m above sea level. Rock formations characterize the interior of the island.