Administratively, Belarus is divided into six oblasts: Brest, Vitebsk, Gomel, Grodno, Minsk, Mogilev and the City of Minsk as a separate administrative area.
States and Administrative Structure
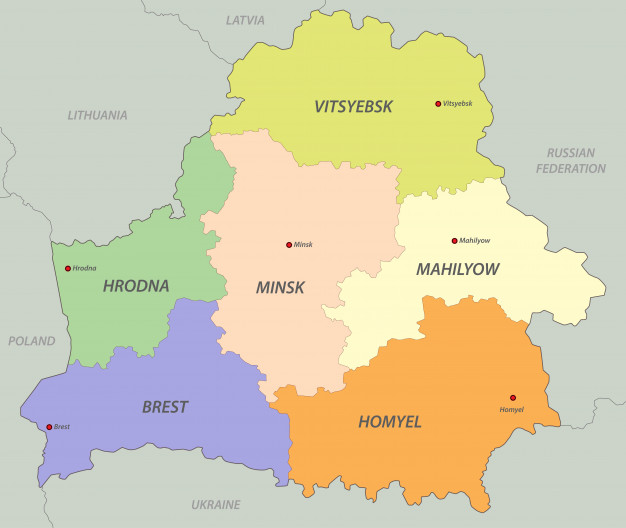 The oblasts are divided into 118 districts, 103 towns, 111 urban villages, with the towns broken down into the following: republic-subordinated towns – 1, oblast-subordinated towns – 37, district-subordinated – 65.
The oblasts are divided into 118 districts, 103 towns, 111 urban villages, with the towns broken down into the following: republic-subordinated towns – 1, oblast-subordinated towns – 37, district-subordinated – 65.
Brest Oblast
It is situated in the south-west of the Republic of Belarus. It borders on Poland in the west, and on Ukraine in the south. It occupies 15.7% of the country’s overall territory, with a population of 14.7%. The oblast capital is Brest (300 thousand people).
The oblast contains 16 districts, 225 rural soviets, 20 towns (including 5 oblast-subordinated ones), and 9 urban villages.
The main industries are food, light and machine-building, which account for almost 2/3 of the overall industrial output. The other developed industries include power engineering, forestry, woodworking, pulp and paper, flour and cereals and feed mill industries.
Agriculturally, the oblast is specialized in meat and dairy livestock farming, production of potatoes, grain-crops, white beets and vegetables.
The oblast has minerals that allow industrial production to develop using the local natural resources. These are building stone, low-melt and heat-resistant clays; glass, molding and building sands, peat, sapropel, gravel; also, shale oil and brown coal deposits have been discovered there.
The oblast operates a free economic zone called “Brest". Special customs regulations that are in force in the zone exempt the zone-bound products from customs duties. The products and services produced by the resident companies to be taken out of the zone are also exempt from customs duties.
The transit passage Berlin-Warsaw-Brest-Minsk-Moscow, an extended network of railways and motor roads, and the direct route to Vilnius and Kiev found on the oblast territory facilitate passenger and cargo transportation from the countries of Europe to Russia, Ukraine and other countries.
Furthermore, the oblast has a Brest-based category 1 international all-weather airport that may accept and handle heavy aircraft such as Boeing 747. Internationally important oil and gas pipelines run through the oblast territory.
The oblast also has a national nature reserve “Belovezhskaya Pushcha”, which can boast diverse wildlife. Scholars working in the nature reserve conduct research in the protection and revival of wildlife species, with a view to preserving the unique nature complex typical of Belarus and Europe, and maintaining the natural evolutionary processes.
Vitebsk Oblast
It is situated in the north-east of the country and borders on Lithuania, Latvia and Russia. It occupies 19.3% of the republic's territory, with a population of 13.8%. The oblast capital is Vitebsk (367 thousand people). The oblast contains 21 districts, 249 rural soviets, 19 towns (including 5 oblast-subordinated ones) and 26 urban villages.
Vitebsk Oblast is an industrially developed region, with power engineering dominating the industry segment of the economy. Large power stations - Lukoml Hydroelectric Power Plant and Novolotsk Heat and Power Plant are to be found there. Apart from power engineering, the region's specialization sectors are food, light, fuel and chemical industries.
Most of the districts are specialized in meat and dairy live-stock farming, pig production, flax cultivation, with the areas around Vitebsk, Orsha and Polotsk focusing on poultry farming, fruit and vegetable production.
The oblast has a unique nature complex - the principal part of the Belarusian Lake District. Out of 19 largest lakes of the country, 11 are located in Vitebsk Oblast.
A complex of Braslav Lakes is a unique one. The Braslav District in the basin of the Western Dvina contains 50 natural reservoirs with an area of 130 square kilometers. Rare wildlife species registered in the Red Book of Endangered Species of Belarus can be found in the lakes. The entire complex is of interest as a zone with favorable opportunities for tourism and recreation.
The oblast has a wealth of historic monuments. Polotsk, one of the ancient Eastern Slavic towns, contains many monuments of the history and culture of the Slavic people (Sofia's Cathedral, the Savior and Euphrosinia Church, the Epiphany Church, etc.).
The Vitebsk Oblast provides favorable transportation opportunities, with two international trans-European passages running through its territory (Paris-Moscow, Helsinki-Vitebsk-Gomel-Kiev-Plovdiv) and the gas-main Yamal-Europe.
Grodno Oblast
It is situated in the North-West of Belarus. It borders on Poland in the west, and on Lithuania in the north. It occupies 12 % of the overall territory, with a population of 11.7%. The Oblast capital is Grodno (309 thousand people). The oblast contains 17 districts, 194 rural soviets, 12 towns, including 6 oblast-subordinated ones, and 21 urban villages.
The chemical industry is the leading segment of the Grodno oblast economy. The largest companies of the industry are located in Grodno and Lida. These are the production companies Azot and Khimvolokno, the joint-stock company Lakokraska.
Over a third of the industrial products produced come from food and machine building companies. The articles manufactured by the Neman Glass Factory, which is located in Berezovka, Lida District, have won widespread fame.
The oblast has well-developed agriculture that comprises dairy and meat live-stock farming, pig production, cultivation of potatoes and flax in the east and growing of white beets in the west. Grain-crops occupy an extended area, with poultry farming and vegetable production well developed near larger towns.
One of the Eurasian backbone routes passes through the oblast, which contributes to broader international cooperation. Because Grodna Oblast enjoys a favorable geographical position, it may become an efficient link promoting trade between the countries of Western and Central Europe and the countries of CIS and Asia.
After the infrastructure of the common European transportation links that pass through the oblast will be improved as planned, the oblast will support further expansion of foreign trade relations. The free economic zone Grodnoinvest is underway.
The largest towns are Grodno, Lida, Slonim, Volkovysk, Smorgon, and Novogrudok. Novogrudok is a place where Belarusian statehood emerged. The Grand Duchy of Lithuania that appeared there in the 12-13th centuries united Belarusian lands. Grodno has preserved many historic and architectural monuments, including: a temple dating back to the 13th-16th centuries, the Boris and Gleb Church (16th-19th centuries), a Franciscan Monastery (18th century), etc.
Gomel Oblast
It is situated in the south-east of the Republic. It borders on Russia in the east, and on Ukraine in the south. The oblast occupies 19.5% of the overall territory, with a population of 16.4%. The Oblast capital is Gomel (515 thousand people). The oblast contains 21 districts, 278 rural soviets, 17 towns, including 8 oblast-subordinated ones, and 18 urban villages.
The oblast is one of the industrially advanced regions of the country. In the industry structure, the most prominent sectors are food, ferrous metallurgy and machine building.
These sectors account for almost half of all industrial products manufactured in the region. The region produces almost 90% of all ferrous metallurgy items of the Republic. This industry is represented by Brest Metallurgy Plant in Zhlobin and a hardware plant in Rechitsa.
The oblast also occupies a leading position in terms of fuel, forest, wood-working, pulp and paper, and microbiological industries. Most of the agricultural districts are specialized in meat and dairy live-stock farming, cultivation of grain-crops, lax and potatoes, and poultry farming and horticulture concentrated around larger towns.
Arterial railways that are of republican and international significance pass through the oblast. The large railway junctions are Gomel, Zhlobin, Kalinkovichy.
Gomel is situated at the crossroads of the railways connecting Bakhmach to Vilnius, and Briansk to Brest. A European passage that runs through Gomel branches out to Minsk and Klaipeda and enables freighters from Eastern Ukraine and Central Russia to access specialized sea ports – Klaipeda, Ventspils and Kaliningrad.
The highways St. Petersburg-Kiev-Odessa, Briansk-Kobrin, Gomel-Minsk, Gomel-Mozyr reach all of the district centers of the oblast through a bus transportation system. Air links connect Gomel to Moscow, St. Petersburg, Kiev and many other cities and towns in Russia, Ukraine and Belarus.
Minsk Oblast
It is in the center of Belarus. Together with Minsk, the oblast occupies 19.4% of the territory and has a population of 15.3%.
The oblast contains 22 districts, 307 rural soviets, 22 towns, including 8 oblast-subordinated ones, and 20 urban villages.This is the only oblast in Belarus that does not border on any foreign states, but due to the most important transportation passages running through its territory, it can be used to further beneficial economic ties with the countries of CIS and beyond.
Industrially, the most prominent sectors are machine building and chemical industry. Also, companies that process agricultural produce are widespread in the region. Nationwide, the oblast holds the first place in terms of products produced by the food, flour and cereals and feed mill industries.
The territory of the oblast contains proven deposits of minerals, with some being developed now. The most important minerals found there include potassium and mine salts, peat, construction materials, sapropels, chalk, shale oil, iron ores, mineral waters, etc.
Most of the agricultural districts focus on dairy and meat live-stock farming, pig production, cultivation of potatoes together with lax, and with beet growing in the south-west. Around the City of Minsk and near the other large towns the agricultural companies are additionally specialized in the growing of fruits and vegetables; also, large poultry farms and companies can be found there.
The natural complex of the oblast can support a wide range of recreational and tourist facilities.
The Naroch group of lakes in Miadel district has excellent conditions favoring recreation and medical treatment activities; there is also a part of the Belarusian Poozerye – the “Blue Lakes” Reserve. Also, the oblast has the principal part of the Berezino biosphere reserve, where typical and unique natural landscapes are maintained, the related natural processes and phenomena are studied, and scientific foundations of nature and environmental education are developed.
Mogilev Oblast
It is in the center of the eastern part of Belarus and borders on Russia. The oblast occupies 14% of the overall territory, with a population of 12.2%. The Oblast capital is Mogilev (371 thousand people). The Oblast contains 21 districts, 195 rural soviets, 13 towns, including 5 oblast-subordinated ones, and 12 urban villages.
The chemical and petrochemical complex occupies the leading place in the industry of the oblast. In terms of chemicals and petrochemicals produced, the oblast is ahead of all the other regions of the country. This industry sector is aimed at producing man-made fiber, organic synthesis products, tires and rubber products.
The food industry, machine building and power engineering occupy a considerable place in the industrial output of the oblast. In the machine building and metalworking production, automobile, agricultural and construction and road machine building are of major importance.
The major minerals on the territory of the oblast are cement and lime raw materials, peat, phosphorites, chalk, building sands and sand and gravel material, dolomites and mineral waters.
The local raw materials are successfully used to produce construction materials and other products. The construction material industry is represented by such enterprises as Krichev Cement and Slate Combine, Belarusian Cement Plant in Kostiukovichi, companies that produce silicate products, reinforced concrete frames, precast concrete, construction materials; brick plants, and glass works in Glush and Yelizovo.
The agricultural districts are specialized in dairy and meat live-stock farming, pig production and flax cultivation. Grain and feed crops, and potatoes occupy an extended area. Around the towns the agricultural companies are additionally specialized in poultry farming and vegetable growing.
An extended network of railways and motor roads that run through the oblast links it to the industrial centers of Belarus and the regions of Russia, Ukraine and Baltic States.
Three arterial railways pass through the oblast: from north to west one that connects Orsha to Zhlobin fron north-west to south-east one that links Orsha and Unecha, and from east to west one that links Yaroslavl and Baranovichi. Most of the motor roads in the oblast can be found in the western districts and some southern districts.
The most important roads that pass there are as follows: St. Petersburg-Kiev, Mogilev-Minsk, Mogilev-Bobruisk and Minsk-Zhlobin.